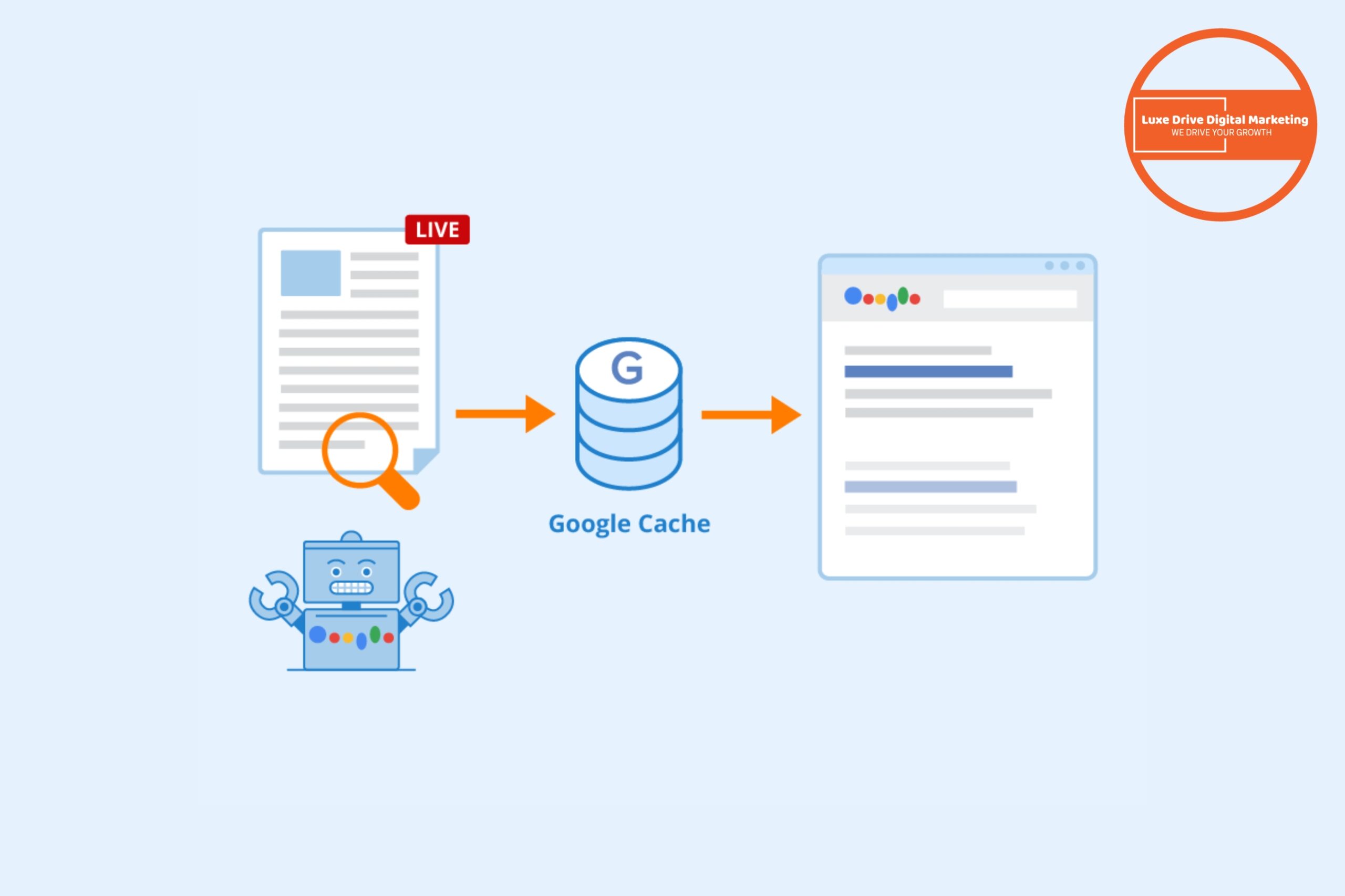
Google cache is a critical aspect of how search engines interact with your website. This stored version of your web pages helps Google understand your content and can be a lifesaver when your live page is temporarily unavailable. Ensuring Google is caching your website correctly is essential for optimal SEO performance and visibility in search results.
What is Google Cache and Why Does it Matter for SEO?
Google cache is essentially a snapshot of your webpage taken during Googlebot’s last crawl. This cached version serves multiple purposes in the SEO ecosystem. When Google crawls your site, it stores a copy of each page in its cache, which it can reference when determining search rankings.
The cache matters significantly for SEO because it represents how Google sees and interprets your content. If there are discrepancies between your live page and the cached version, it could indicate issues with how search engines understand your website. These cache issues might negatively impact your search engine results and overall SEO efforts.
Additionally, the Google cache version provides a backup of your content that users can access if your website experiences downtime. This improves user experience by ensuring your information remains accessible even when technical problems arise with your site’s server.
How Do I View Google’s Cached Version of My Website?
Viewing the cached version of your website is straightforward using several methods. The most direct approach is through Google search results. Simply search for your website using the query “site:yourdomain.com,” then click on the three dots next to the URL in the search result and select “Cached.”
Alternatively, you can use the specific cache: operator in Google search. Type “cache:yourdomain.com/page” into the search bar, and Google will display the most recent cached version of that webpage. This method allows you to check specific web pages without navigating through search results.
For Chrome users, several cache viewer extensions are available that streamline this process. These tools add functionality to your browser that makes viewing cached pages just a click away. The web cache viewer extensions can save time when you’re regularly monitoring how Google is caching your website correctly.
Remember that the cached version you’re seeing represents how Googlebot last saw your page, including its CSS and JavaScript rendering. This insight is invaluable for understanding how search engines interpret your site’s structure and content.
Why Isn’t Google Caching My Website?
If you discover that Google hasn’t cached your website, several factors could be responsible. One common reason is that your site’s robots.txt file might be blocking Googlebot from crawling your pages. Check your robots.txt file to ensure it’s not preventing access to important content.
Another possibility is that your website is too new. Google needs time to discover, crawl, and index new websites before creating cached versions. If you’ve recently launched your site, patience may be all that’s needed as Google completes its indexing process.
Technical issues can also prevent caching. If your server returns error codes when Googlebot attempts to crawl your pages, Google won’t be able to create a proper cache. Similarly, if your page load times are extremely slow, Googlebot might time out before fully rendering the content.
Pages with the “noindex” meta tag or header will not be cached, as Google respects these directives not to index the content. Check your source code to ensure you haven’t inadvertently included these tags on pages you want cached.
What Information Can I Learn from Google’s Cached Version?
The cached version of your website reveals crucial information about how Google interprets your content. By examining the cached page, you can see exactly what text Google has indexed, which can help identify any content that might be missing from Google’s view.
You can also verify that your important on-page SEO elements are visible to Google. This includes checking that your headings, meta descriptions, and structured data are properly recognized in the cached version. If these elements aren’t appearing correctly, it could hamper your SEO efforts.
The cached version shows how Google renders your JavaScript and CSS. If you’re using these technologies extensively, the cache can reveal whether Google is properly executing your code or if there are rendering issues that need addressing.
Lastly, the timestamp on the cached page indicates when Google last crawled that specific URL. This information helps you understand how frequently Google is visiting and updating its cache of your website, which can inform your content update strategy.
How Often Does Google Update Its Cache?
Google doesn’t follow a fixed schedule for updating its cache. The frequency depends on various factors, including your website’s authority, how often you publish new content, and the overall popularity of your site.
High-authority websites with frequent updates might see their cache refreshed daily or even multiple times per day. In contrast, smaller sites or pages that rarely change might only be recached every few weeks or months.
You can influence this frequency by regularly publishing fresh, high-quality content. When Google detects that your website is consistently updated with valuable information, it may increase its crawling frequency, leading to more frequent cache updates.
The Google Search Console provides insights into how often Googlebot is crawling your site. By monitoring these statistics, you can gauge whether Google is visiting frequently enough to maintain an up-to-date cache of your constantly evolving content.
What Are the Different Types of Google Cache Views Available?
When viewing a cached web page, Google offers three different versions: Full, Text-only, and Source. Each provides unique insights into how Google interprets your website.
The Full version displays the page as Google rendered it during its last crawl, including images, CSS styling, and JavaScript functionality. This view most closely resembles what users see when visiting your live site and helps you understand if Google is properly rendering your design elements.
The Text-only version strips away all formatting, images, and scripts to show just the textual content that Google has indexed. This view is particularly useful for SEO analysis as it reveals exactly what content Google considers most important on your page.
The Source view shows the raw HTML that Google retrieved during its crawl. This can help web developers identify any technical issues with how Google is processing your source code. By comparing this with your current source code, you can spot discrepancies that might affect your site’s performance in search results.
How Can I Fix Issues with Google’s Cached Version of My Site?
If you discover problems with how Google is caching your website, several troubleshooting steps can help resolve these issues. First, use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to request a recrawl of problematic pages. This tool provides detailed information about how Googlebot sees your page and can expedite the updating process.
For rendering problems, ensure your website doesn’t rely on technologies that Googlebot might struggle with. While Google has improved its ability to render JavaScript, complex implementations can still cause issues. Consider implementing server-side rendering for critical content to ensure it’s properly cached.
If important content is missing from the cached version, check that it’s not hidden behind user interactions like clicks or hovers. Googlebot may not trigger these interactions during crawling, causing the content to be missed in the cached version.
For sites with dynamic content, implement proper caching headers to guide how Google and other search engines should cache your pages. The “Cache-Control” and “Expires” HTTP headers can specify how long content should remain cached before being refreshed.
What Tools Can Help Check if Google is Caching My Website Correctly?
Several tools can help monitor and analyze how Google is caching your website. Google Search Console is the primary tool provided by Google itself, offering insights into indexing status, crawl errors, and mobile usability issues that might affect caching.
Third-party cache checker tools can automate the process of checking cached versions across multiple pages. These website cache checkers save time when monitoring large sites and can alert you to pages that haven’t been cached properly.
The Wayback Machine from Internet Archive provides historical cached versions of web pages, allowing you to compare how your site has been cached over time. While not directly related to Google’s cache, this tool offers valuable historical context.
Browser extensions like “Web Developer” for Chrome include features to quickly view cached versions of pages you’re browsing. These extensions streamline the process of regular cache checking as part of your ongoing SEO maintenance.
How Does Google Cache Impact My Website’s SEO Performance?
The relationship between Google cache and SEO performance is multifaceted. First, the cached version reflects what Google has indexed and how it understands your content, directly influencing your rankings in search results.
If the cached version differs significantly from your live page, it might indicate that Google isn’t properly interpreting your content, potentially hurting your rankings. Consistency between your live site and its cached version is crucial for optimal SEO performance.
The cache also affects how quickly Google recognizes and rewards content updates. If your site isn’t being cached frequently, new content or improvements might take longer to positively impact your rankings. Regular monitoring of cache updates can help you understand this aspect of SEO timing.
For technical SEO, the cached version reveals how Googlebot handles your site’s JavaScript, CSS, and HTML structure. Identifying and fixing rendering issues visible in the cache can improve how search engines interpret your site, potentially boosting rankings.
Can I Prevent Google from Caching Specific Pages on My Website?
Yes, you can prevent Google from caching specific pages if necessary. The most direct method is to use the “noarchive” meta tag in the head section of your HTML. Adding <meta name="robots" content="noarchive"> tells search engines not to store a cached version of that page.
For more granular control, you can target specific search engines. For example, <meta name="googlebot" content="noarchive"> prevents only Google from caching the page while allowing other search engines to do so.
Alternatively, you can use the HTTP header “X-Robots-Tag: noarchive” to achieve the same result. This method is particularly useful when you can’t modify the HTML directly, such as with PDF files or other non-HTML content.
Remember that preventing caching doesn’t prevent indexing. Your pages can still appear in search results even if Google doesn’t maintain a cached version. This approach is useful for time-sensitive content or pages with frequently changing information where an outdated cache might confuse users.
Key Points to Remember About Google Cache and Website Performance
- Cache Monitoring is Essential: Regularly check how Google is caching your website to identify potential SEO and rendering issues.
- Cache Frequency Matters: More frequent caching indicates Google finds your content valuable and keeps your indexed content fresh.
- Technical Rendering: The cached version reveals how Googlebot interprets your JavaScript, CSS, and overall page structure.
- Troubleshooting Tool: Use the cache to diagnose why certain content might not be ranking as expected.
- User Experience Backup: Google cache serves as a backup when your live page is temporarily unavailable, improving overall user experience.
- SEO Indicator: Discrepancies between your live site and cached version can signal potential SEO problems.
- Crawl Budget Optimization: Understanding how Google caches your site helps optimize your crawl budget for better indexing.
Conclusion
Understanding how to check if Google is caching your website correctly is fundamental to successful SEO and optimal search engine visibility. The cached version of your website provides a window into how Googlebot sees and interprets your content, offering invaluable insights for web developers and SEO professionals alike. By regularly monitoring your website cache checker results, you can identify and resolve issues before they negatively impact your search rankings. Remember that the cached web page represents what users and search engines see when interacting with your site, making it a critical component of your digital presence. Whether you’re using Google Search Console’s tools, browser extensions like those available for Chrome, or specialized cache viewer extensions, staying vigilant about how your site is cached ensures that your version of the site aligns with Google’s stored version. This alignment between your live page and the cached content is essential for maintaining strong search result positions and providing the best possible user experience for your visitors.